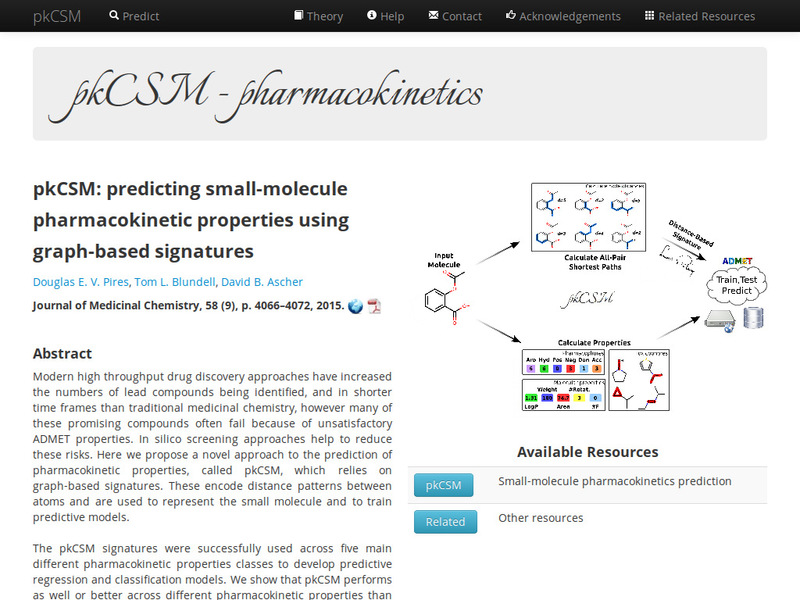
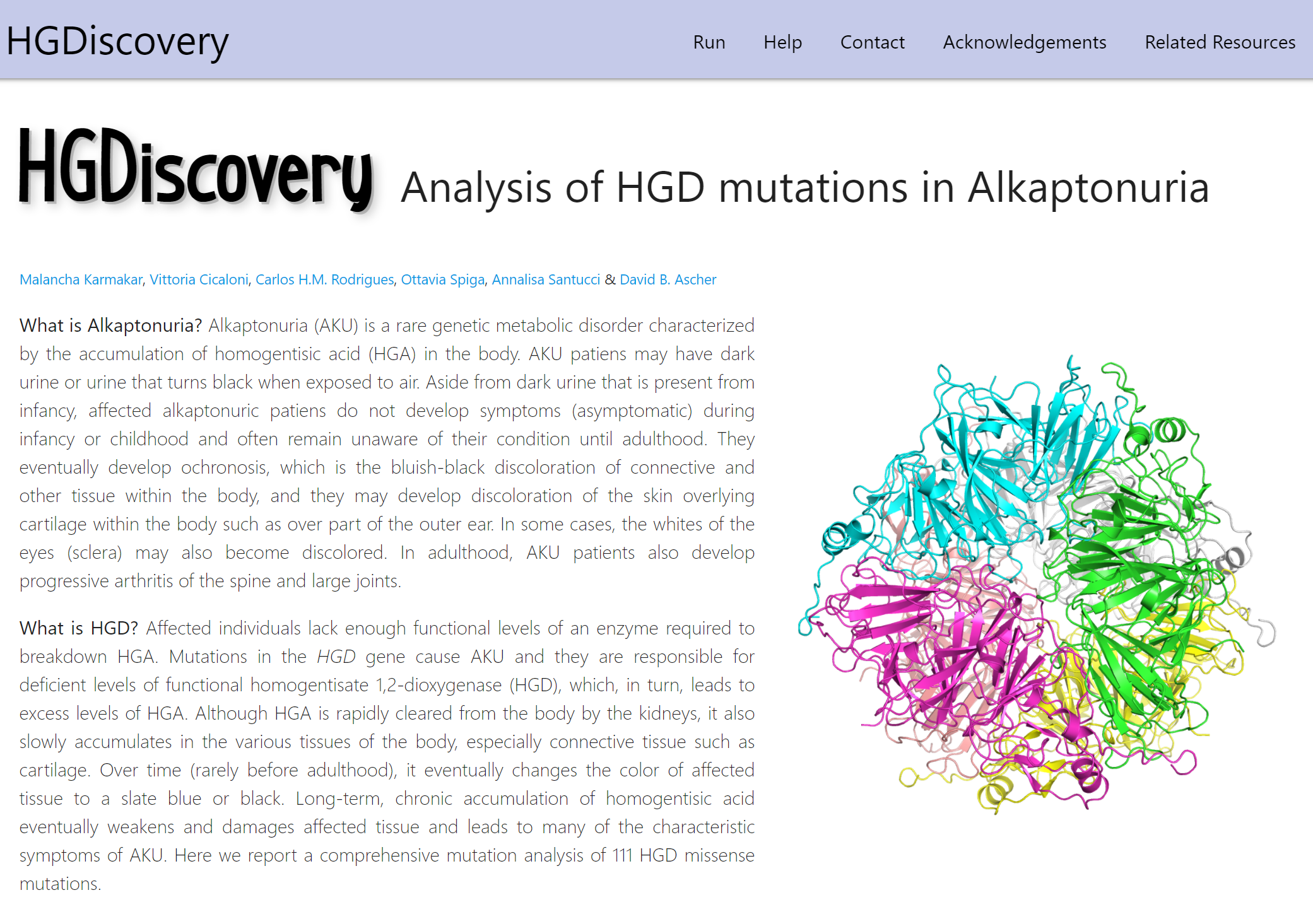
AlzDiscovery perdicts the effects of all possible missense mutations on 21 Alzheimer's Disease related proteins.
Tools
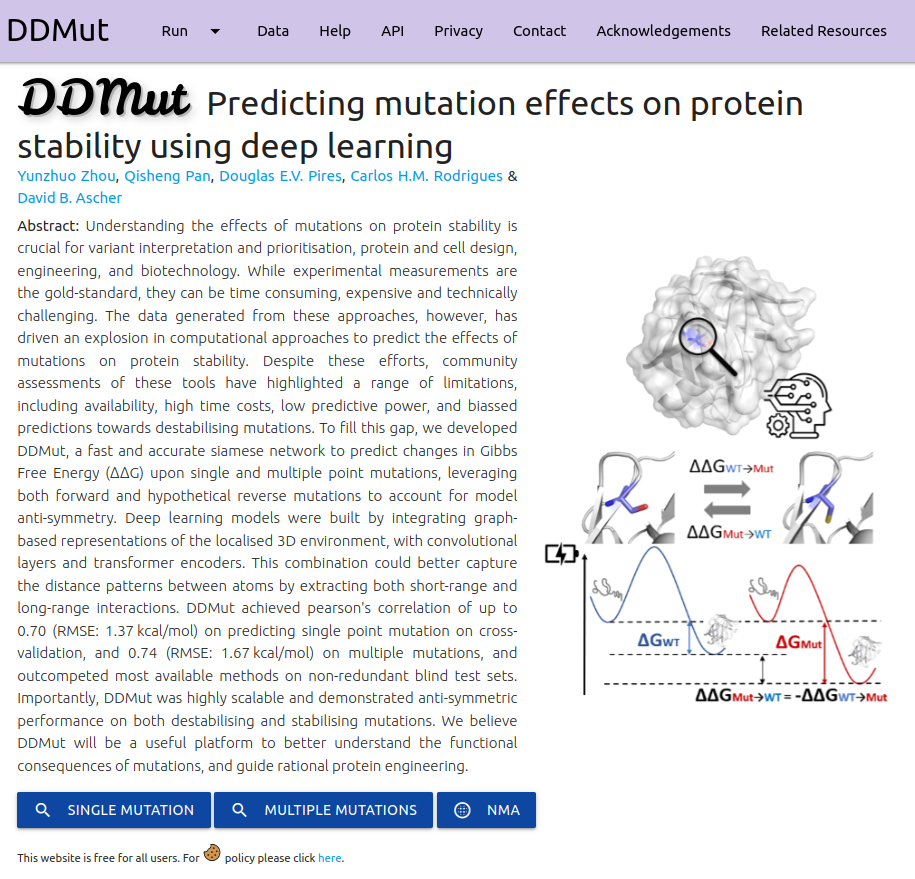
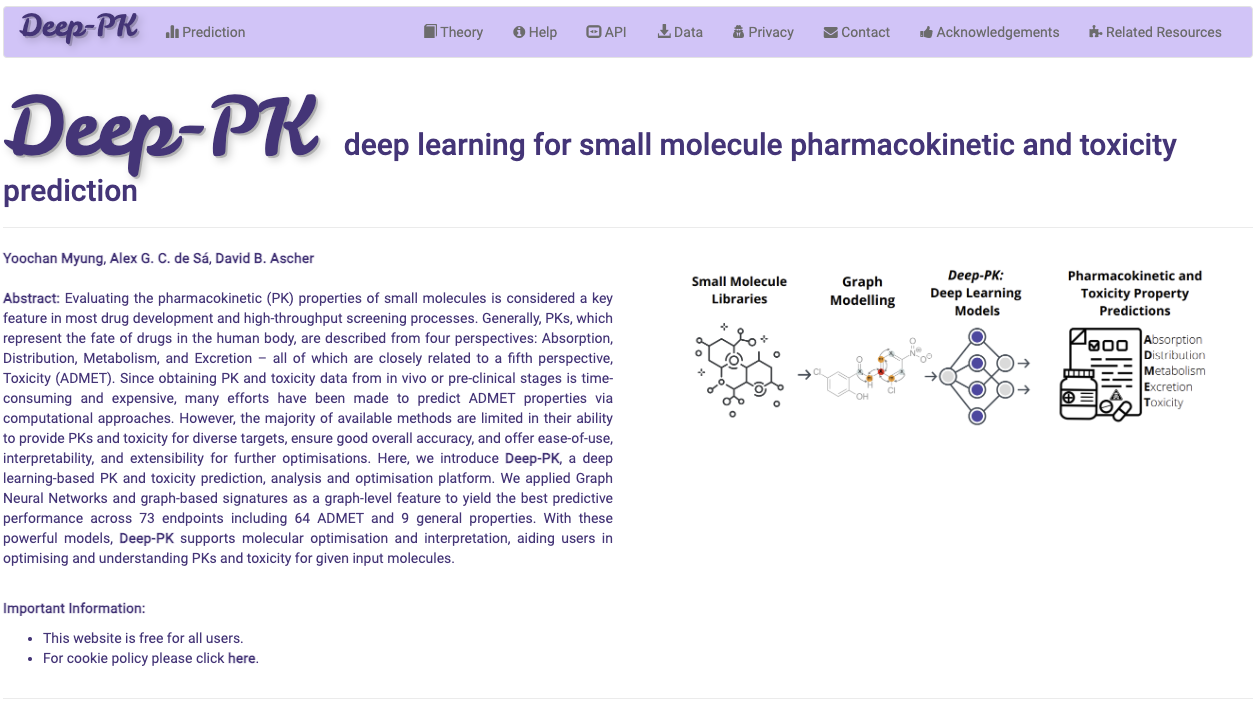
DDMut is a fast and accurate siamese network to predict changes in Gibbs Free Energy (ΔΔG) upon single and multiple point mutations, leveraging both forward and hypothetical reverse mutations to account for model anti-symmetry.
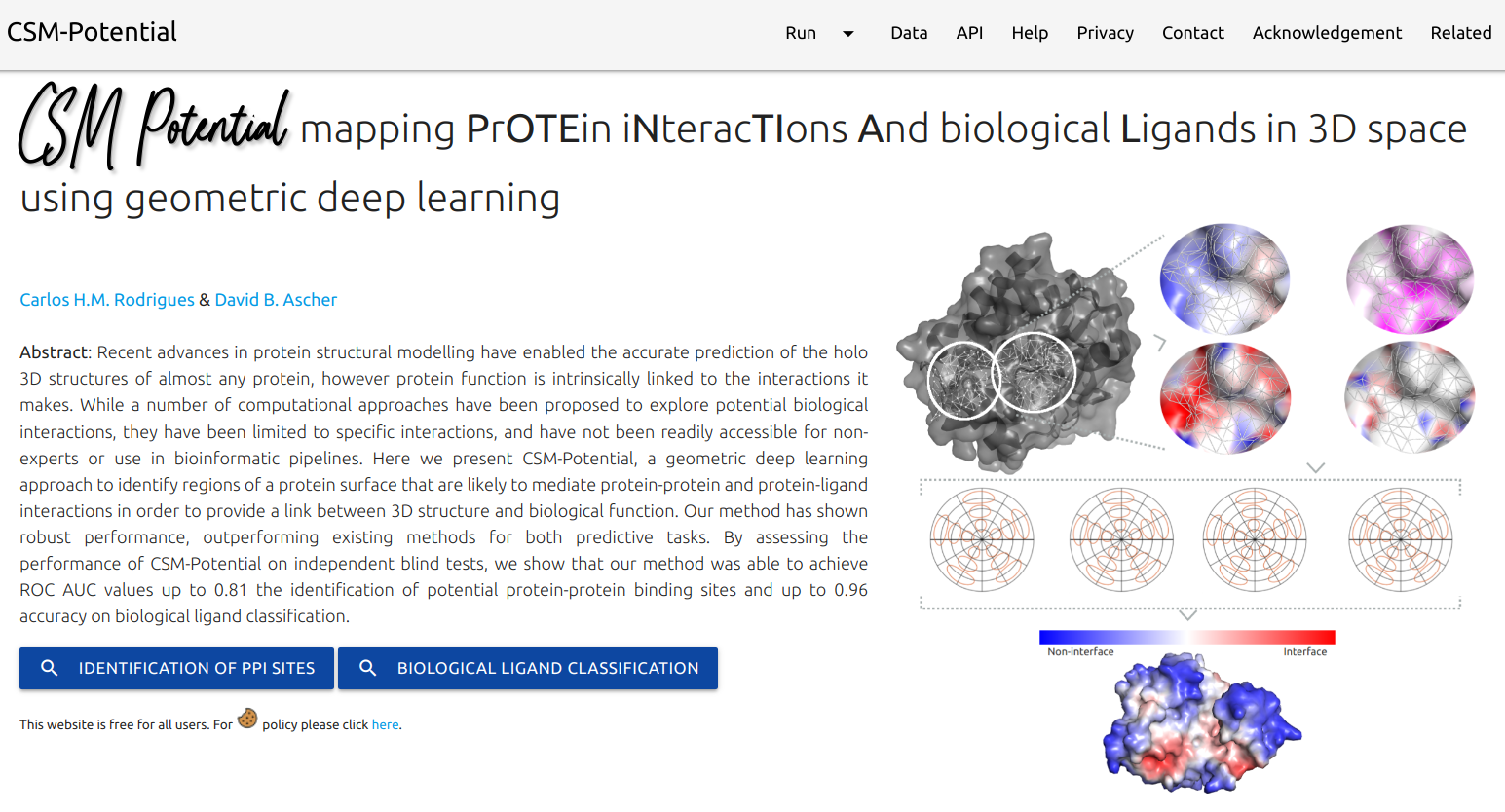
CSM-Potential is a geometric deep learning approach to identify regions of a protein surface that are likely to mediate protein-protein and protein-ligand interactions in order to provide a link between 3D structure and biological function
COVID-3D is an online resource that provides a bridge between the wealth of genomic information being collected on SARS-CoV-2 and their structural and functional consequences, to provide biological insights and help guide therapeutic development efforts.
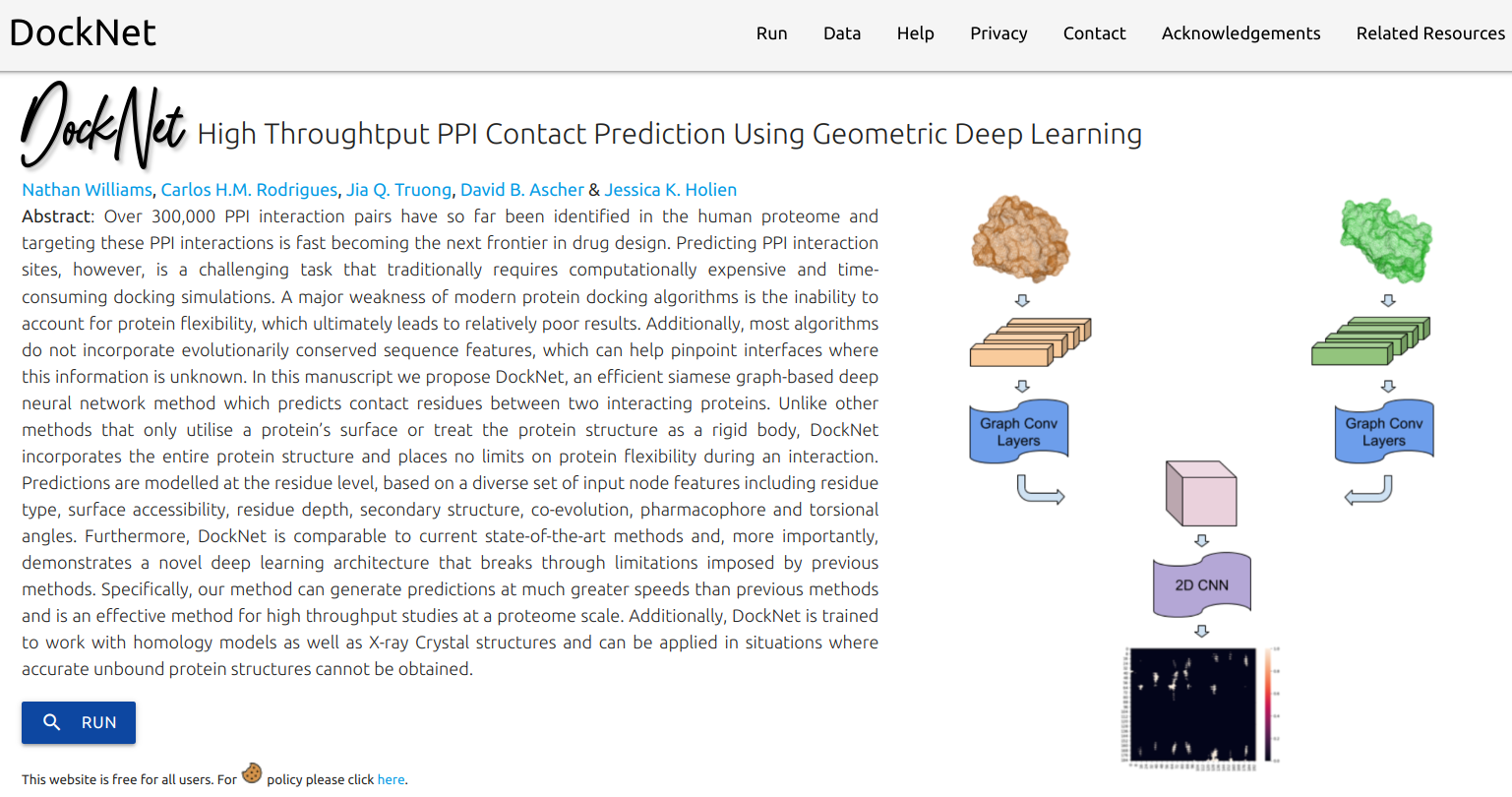
DockNet, an efficient siamese graph-based deep neural network method which predicts contact residues between two interacting proteins. Unlike other methods that only utilise a protein’s surface or treat the protein structure as a rigid body, DockNet incorporates the entire protein structure and places no limits on protein flexibility during an interaction.
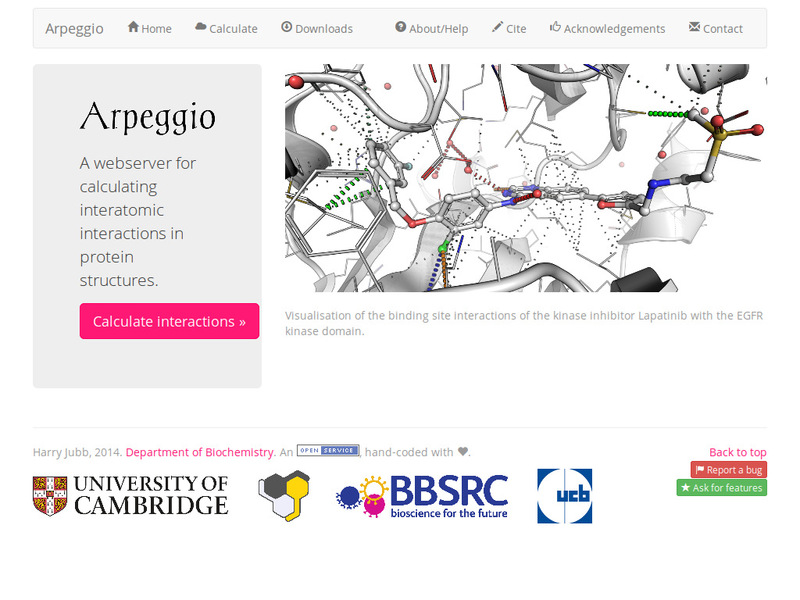
Calculation and visualisation of all molecular interactions between atoms of molecules of interest, including proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates as well as small molecules.
CSM-Toxin is a novel in-silico protein toxicity classifier, which relies solely on the protein primary sequence. Our approach encodes protein sequence information using a deep learning natural languages model to understand the “biological” language, where residues are treated as words and protein sequences as sentences.
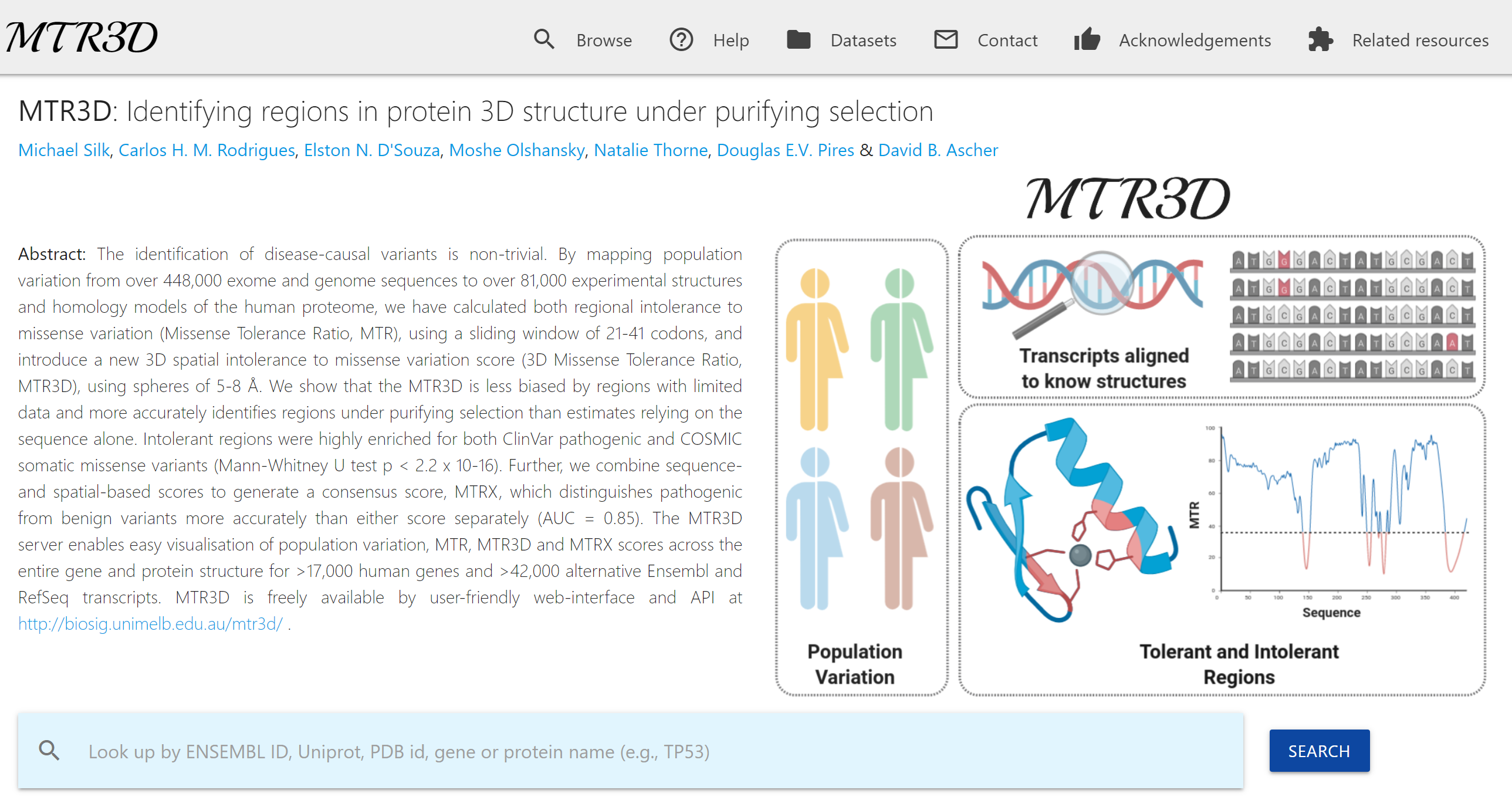
Quantification of the extent of localized purifying selection in protein-coding sequences. The missense tolerance ratio (MTR) summarizes available human standing variation data within genes to encapsulate population level genetic variation.
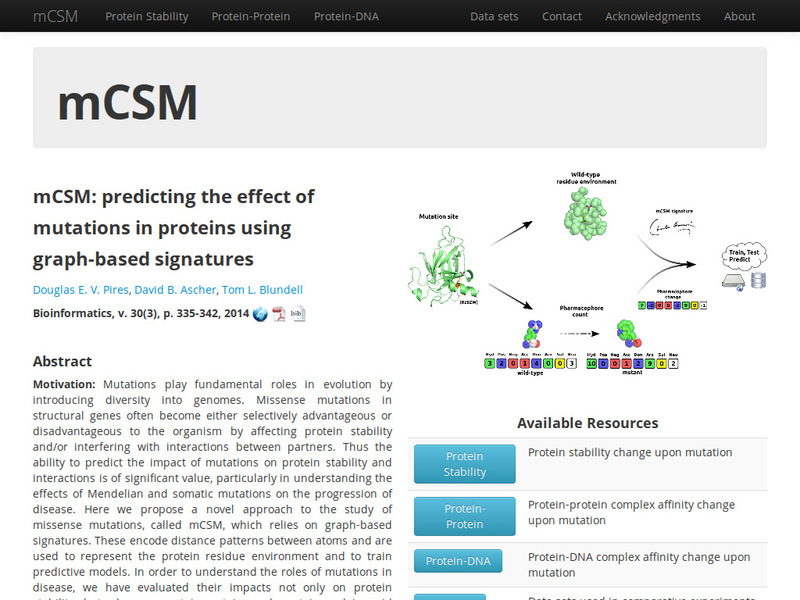
A novel graph-based signature approach for the quantitative prediction of the effects of missense mutations on protein stability.
An integrated computational approach for quantitative prediction of the effects of missense mutations on protein stability.
Analysis and visualisation of protein dynamics using normal mode analysis. Quantitative prediction of the effects of missense mutations on protein dynamics and stability.
Fast and accurate evaluation of the effects of single and multiple point mutations on protein folding, stability, flexibility and conformation by combining protein dynamics and machine learning.
Predicting the effects of mutations in membrane proteins on stability, and whether they are likely to be benign or pathogenic.
A novel graph-based signature approach for the quantitative prediction of the effects of missense mutations on protein-protein binding affinity.
An optimised novel graph-based signature approach for the quantitative prediction of the effects of missense mutations on protein-protein binding affinity.
A scalable and effective machine learning model for accurately assessing changes in protein-protein binding affinity caused by single and multiple missense mutations
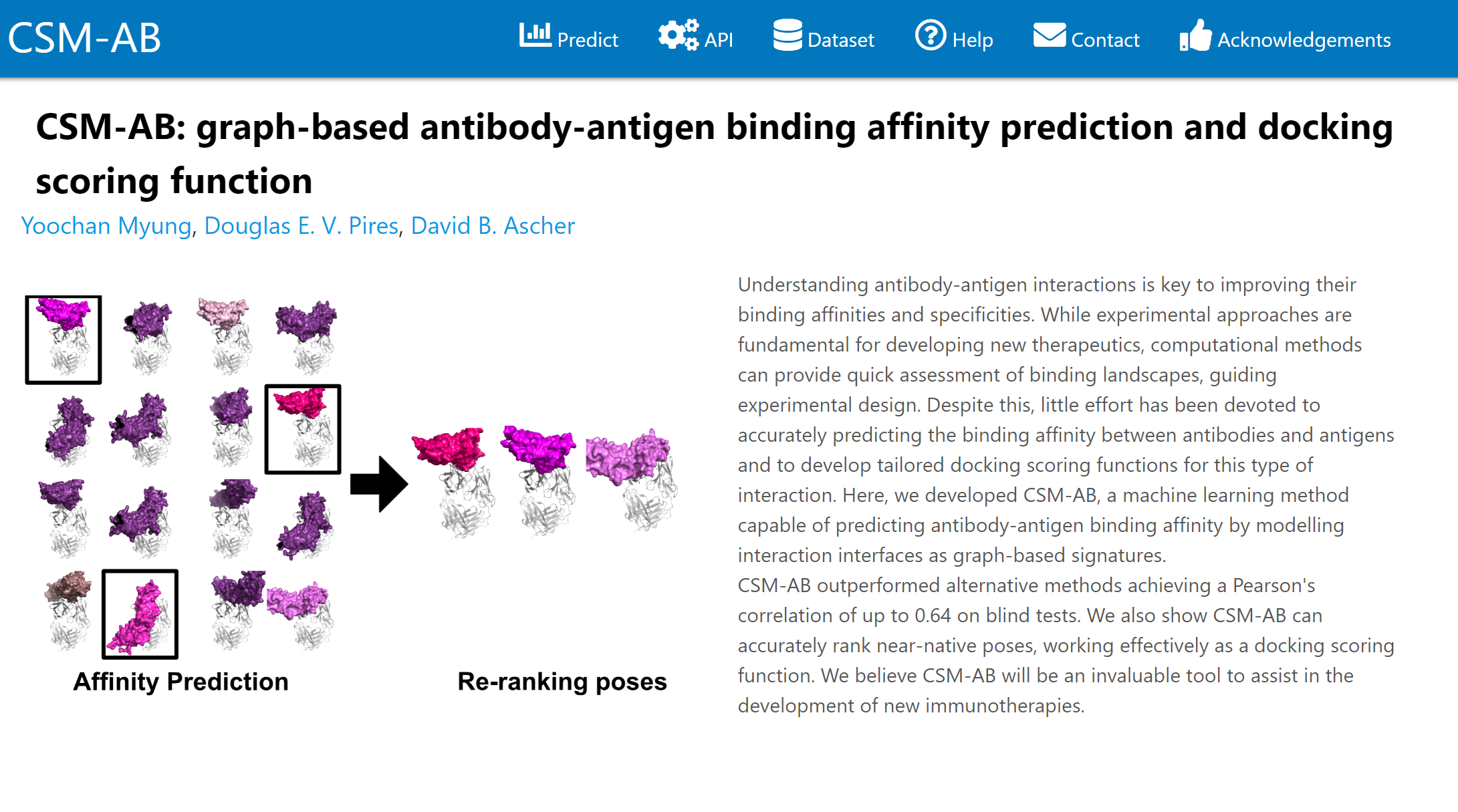
Quantitative prediction of the effects of missense mutations on antibody-antigen binding affinity to guide rational antibody engineering.

Predicting the effects of introducing multiple point mutations on antibody-antigen binding affinity.
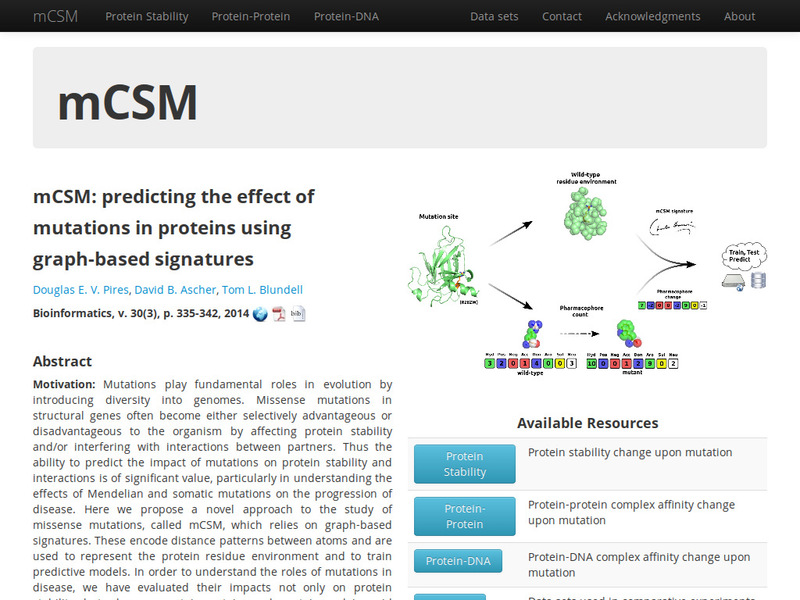
A novel graph-based signature approach for the quantitative prediction of the effects of missense mutations on protein-DNA binding affinity.

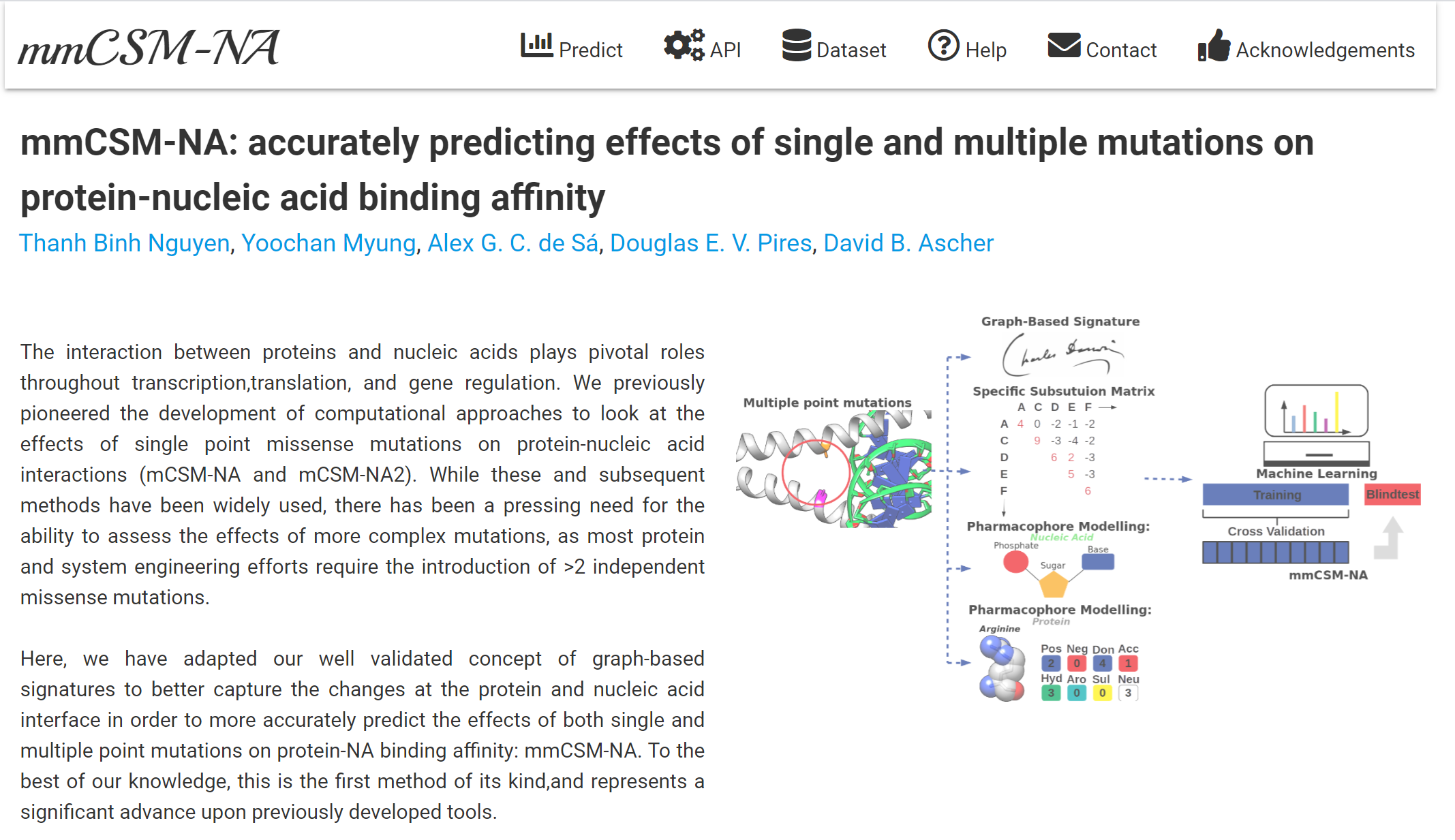
Quantitative prediction of the effects of missense mutations on protein-nucleic acid binding affinities using graph-based signatures.
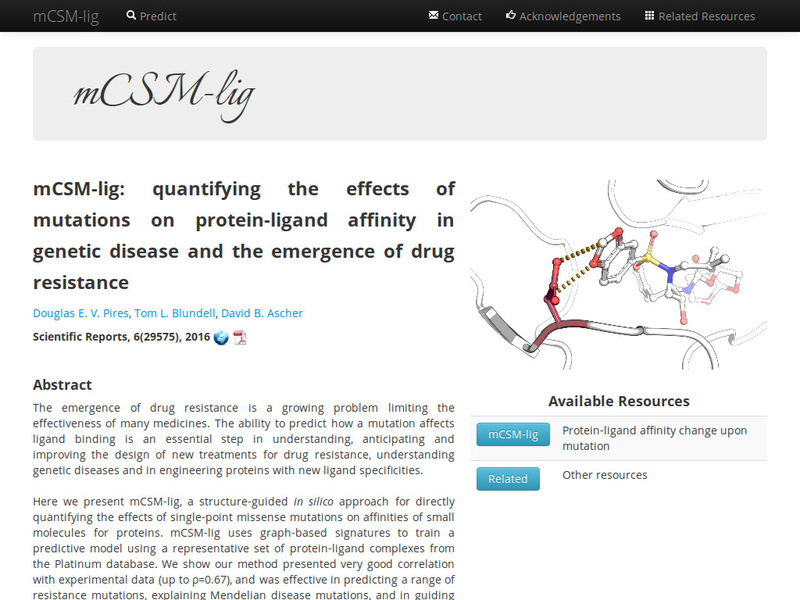
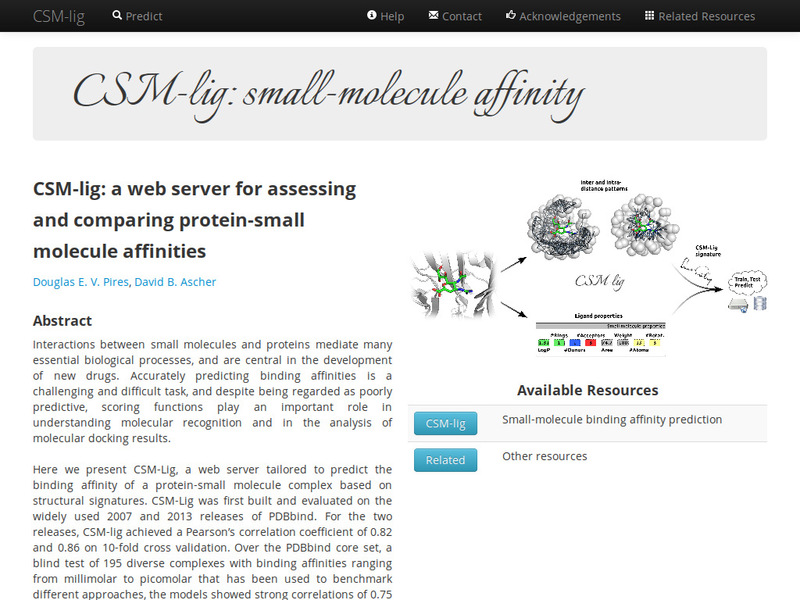
Quantitative prediction of the effects of missense mutations on affinities of small molecules for proteins using graph-based signatures.
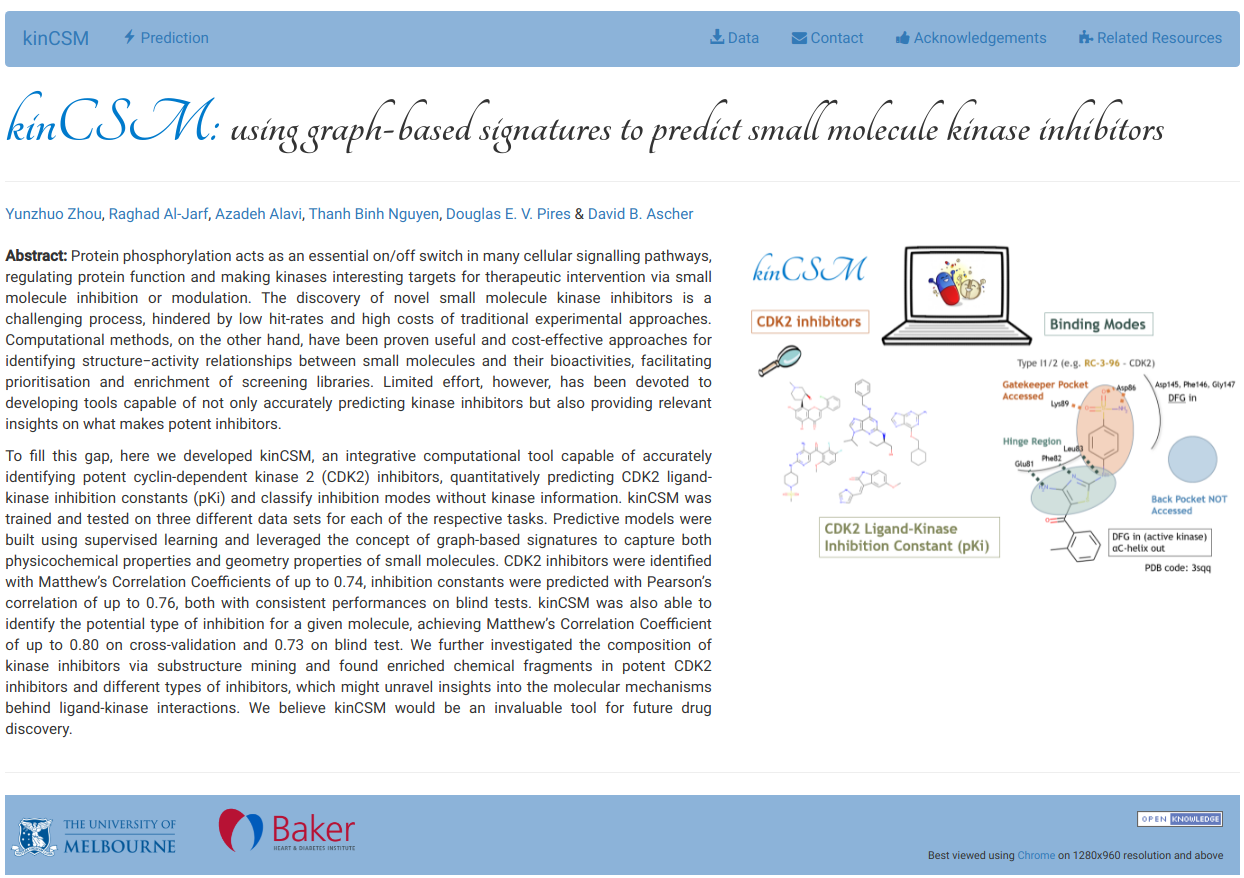
kinCSM is an integrative computational tool capable of accurately identifying potent cyclin-dependent kinase 2 (CDK2) inhibitors, quantitatively predicting CDK2 ligand-kinase inhibition constants (pKi) and classify inhibition modes without kinase informatio
Target and Symptom-based computational Model for miRNA-Disease Association prediction (TSMDA) is a novel machine learning method that leverages target and symptom information and negative sample selection to predict miRNA-disease association.
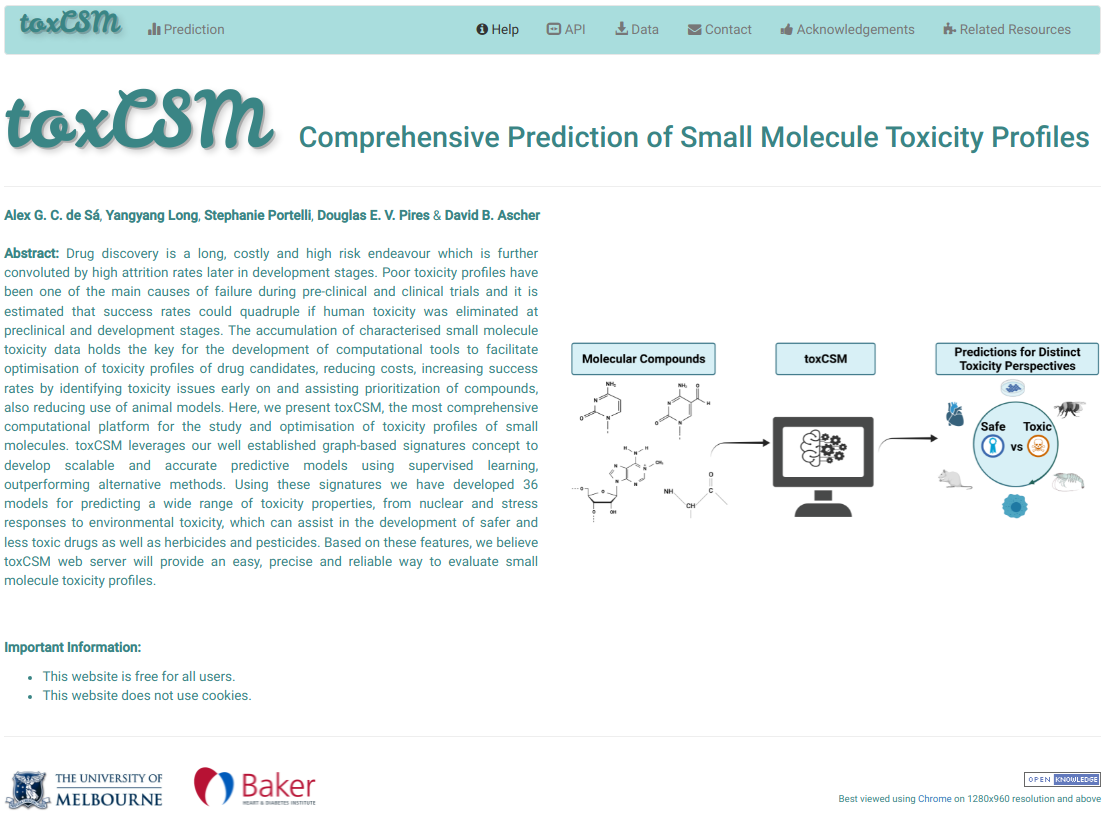
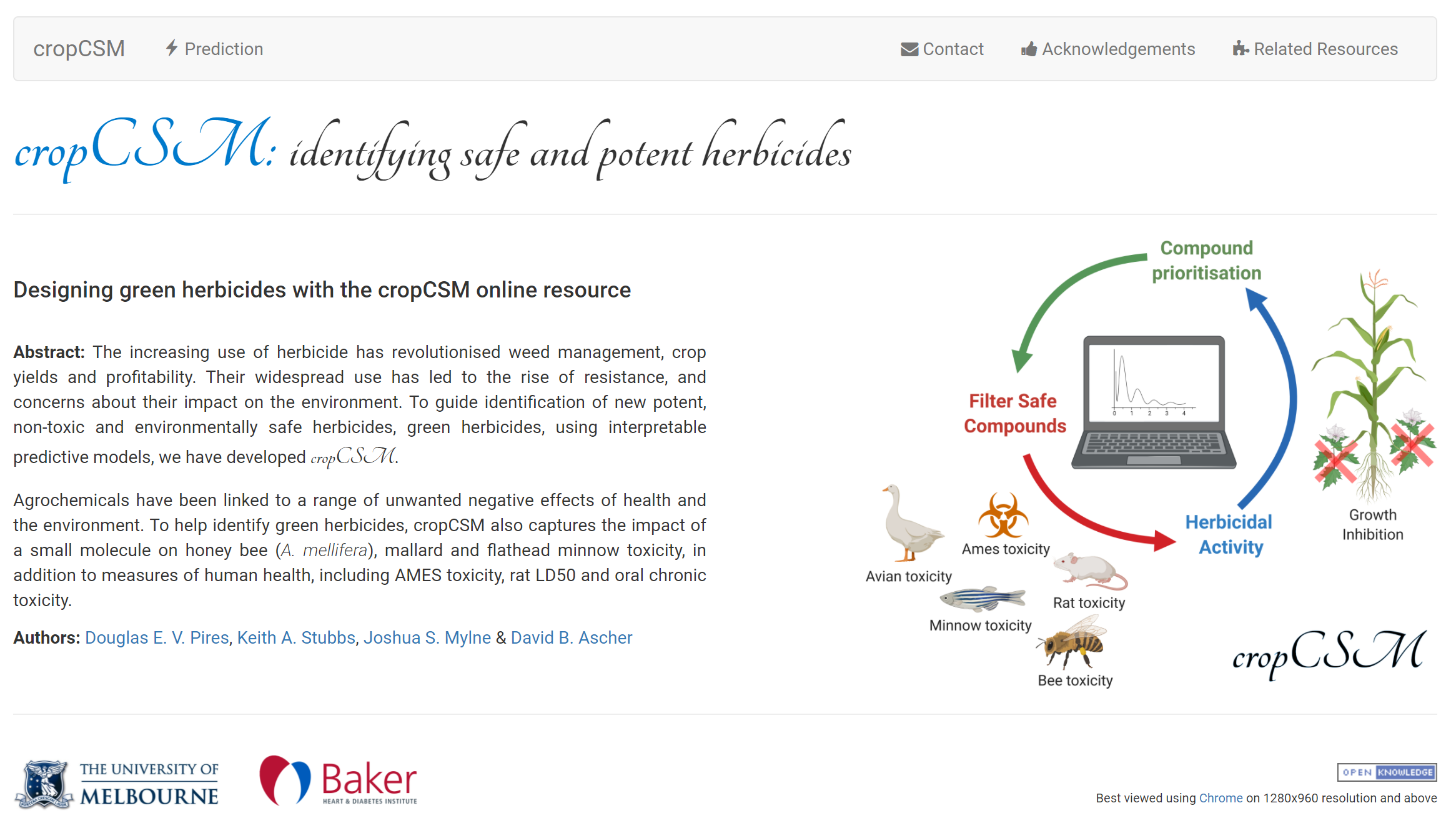
toxCSM leverages on the well-established concepts of graph-based signatures, molecular descriptors and similarity scores to develop 36 models for predicting a range of toxicity properties, which can assist in developing safer drugs and agrochemicals
A graph-based signature approach to rapidly identify compounds likely to be active against Mycobacterium
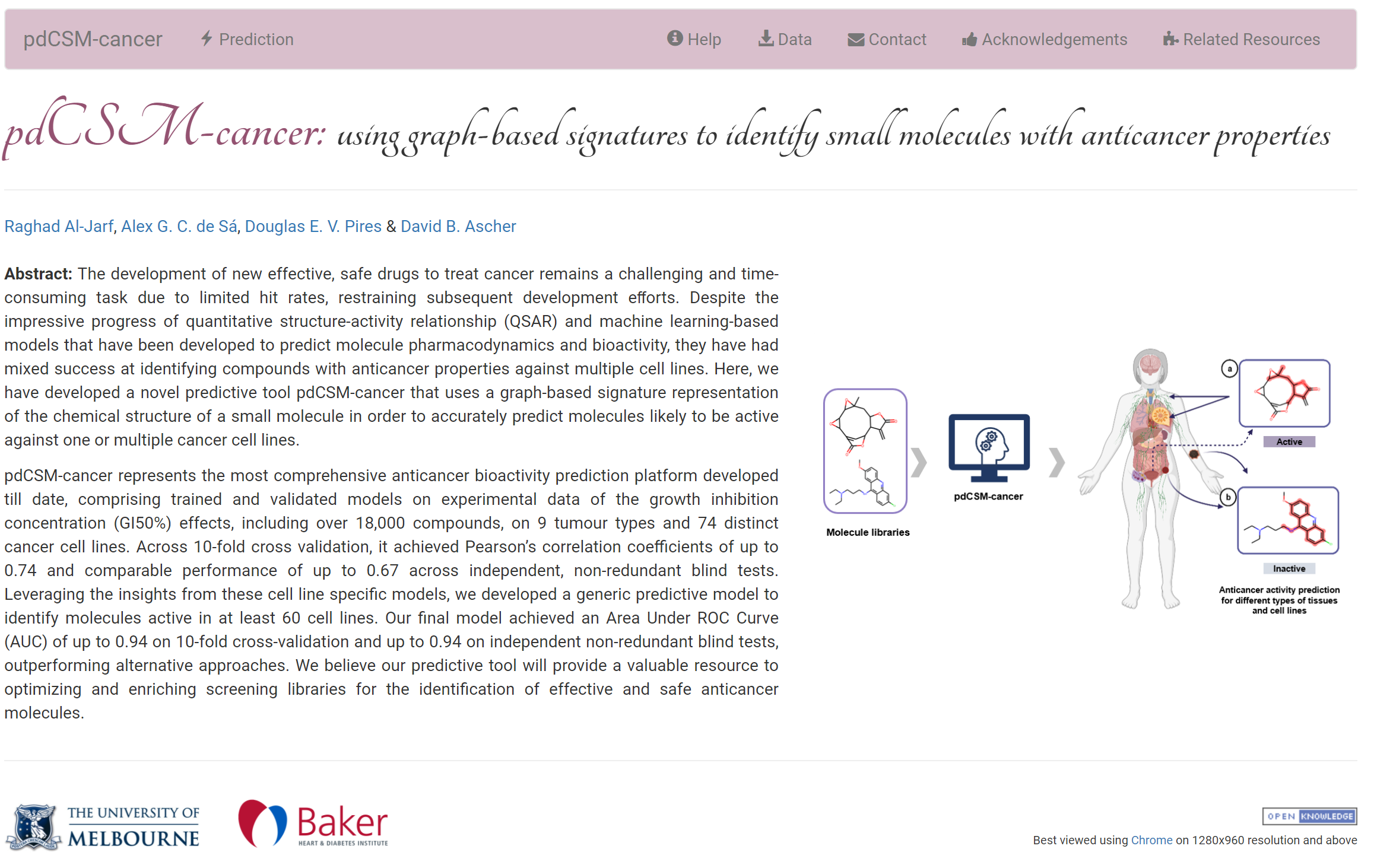
A graph-based signature approach to rapidly identify compounds likely to be active against over 70 different cancer cell lines.
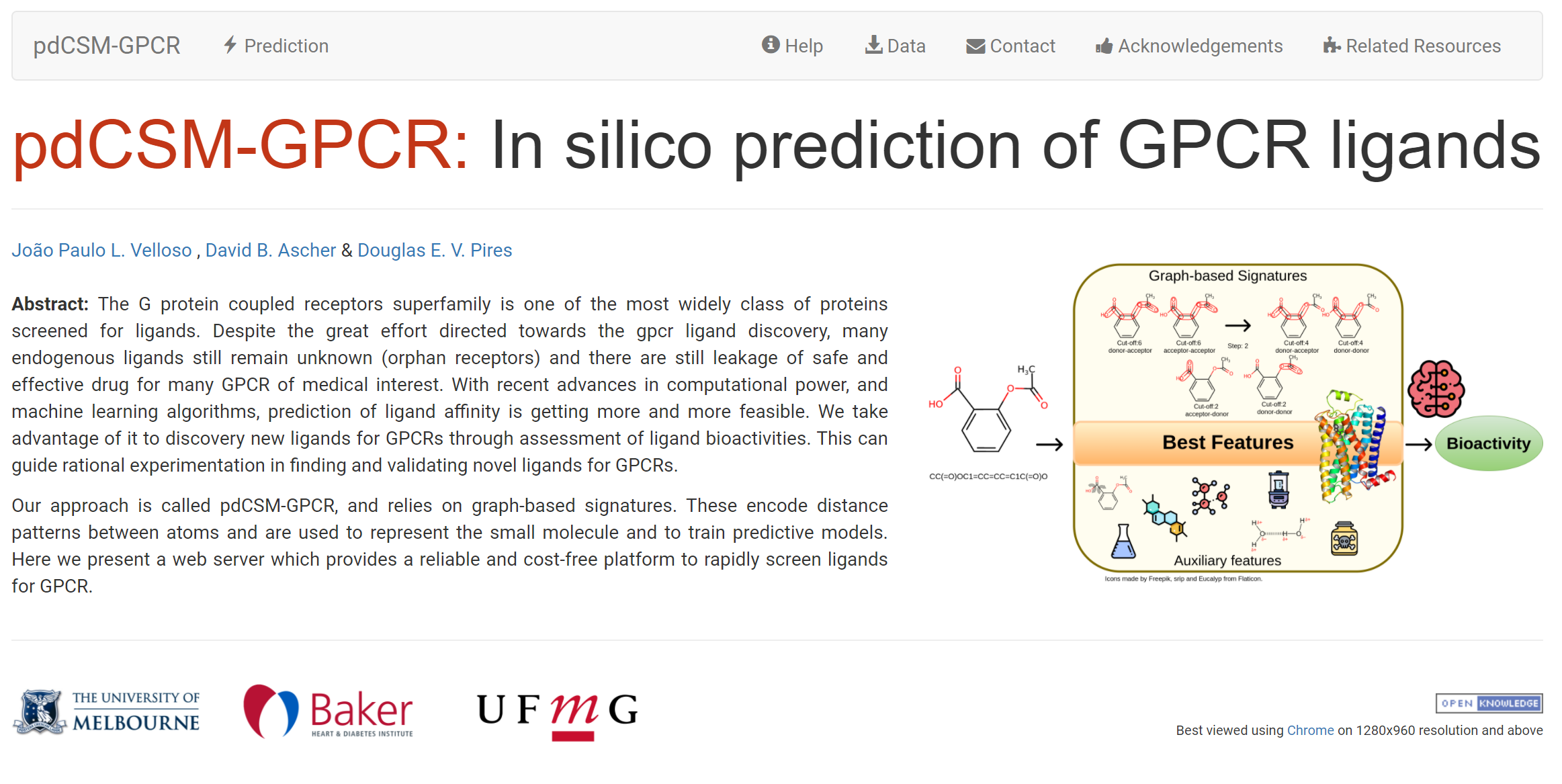
A graph-based signature approach to rapidly identify ligands against 36 major GPCR targets, across 4 classes.
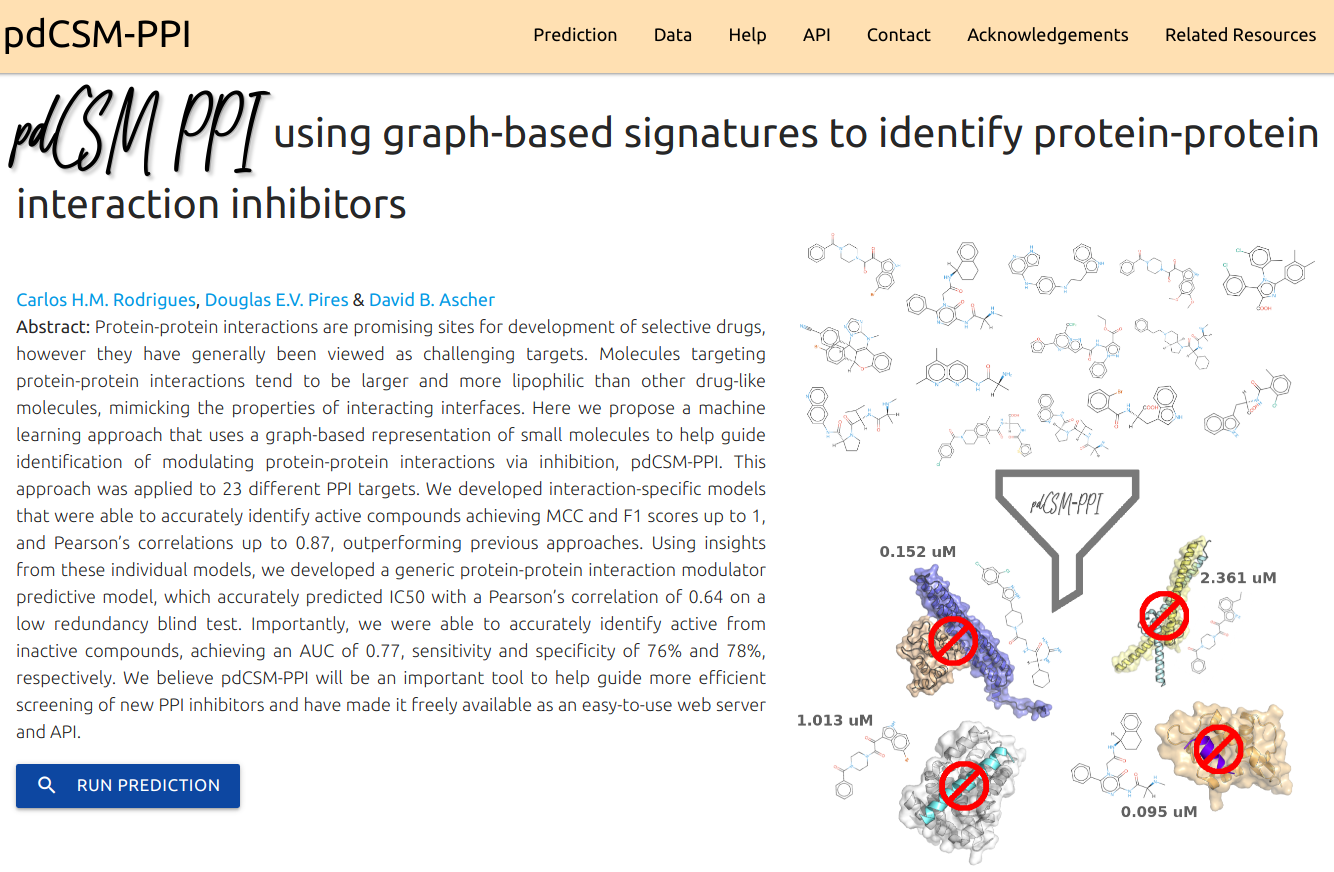
A machine learning approach that uses a graph-based representation of small molecules to help guide identification of modulating protein-protein interactions via inhibition.

To facilitate the further development and evaluation of methods to predict these changes, we have developed ThermoMutDB, a manually curated database containing >14,669 experimental data of thermodynamic parameters for wild type and mutant proteins.
This manually curated, literature-derived database of the effects of over 1,000 mutations protein-ligand binding affinity together with the three-dimensional structures of the complex.
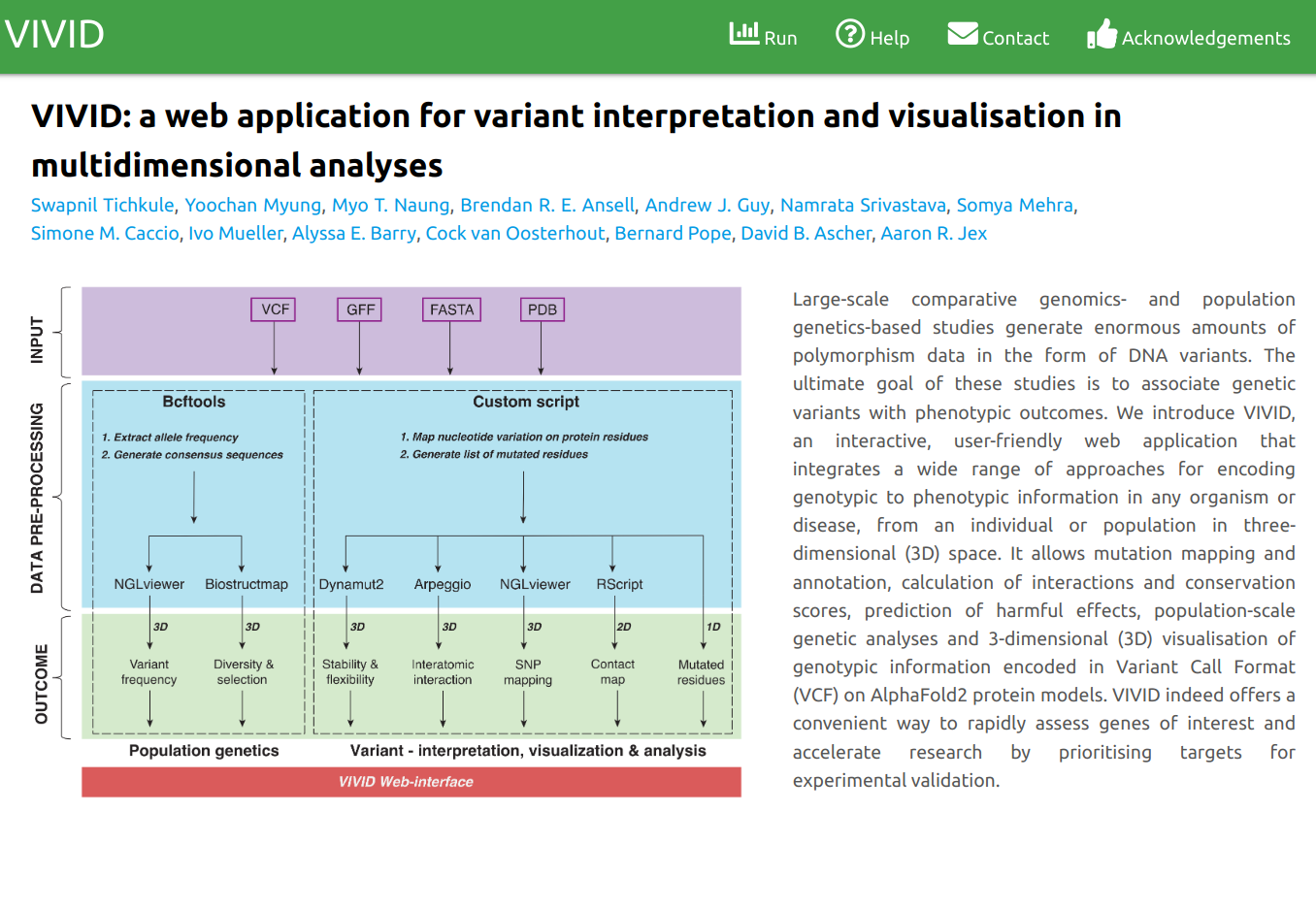
VIVID is an interactive, user-friendly web application that integrates a wide range of approaches for encoding genotypic to phenotypic information in any organism or disease, from an individual or population in three-dimensional (3D) space
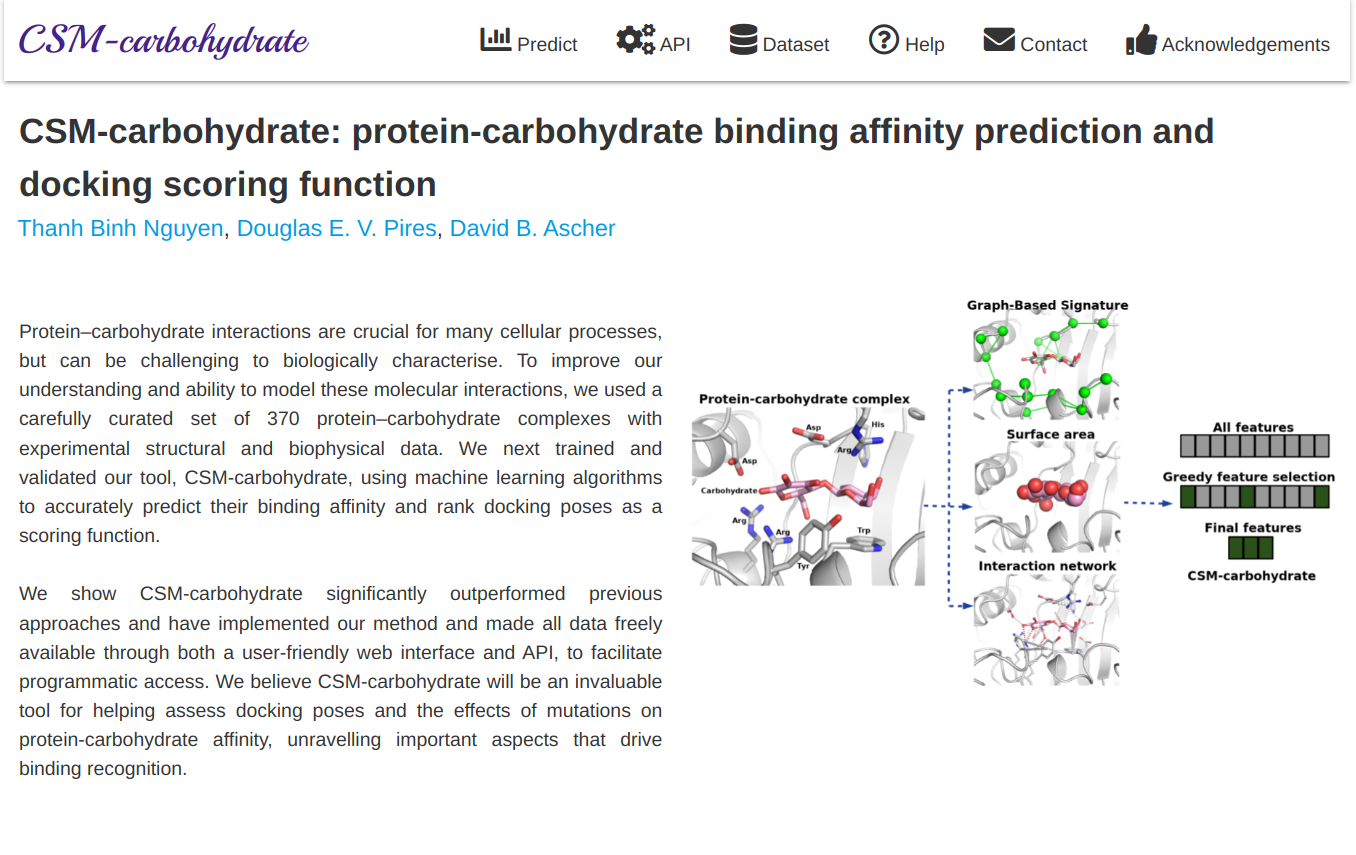
CSM-carbohydrate is a tool for helping assess docking poses and the effects of mutations on protein-carbohydrate affinity, unravelling important aspects that drive binding recognition.
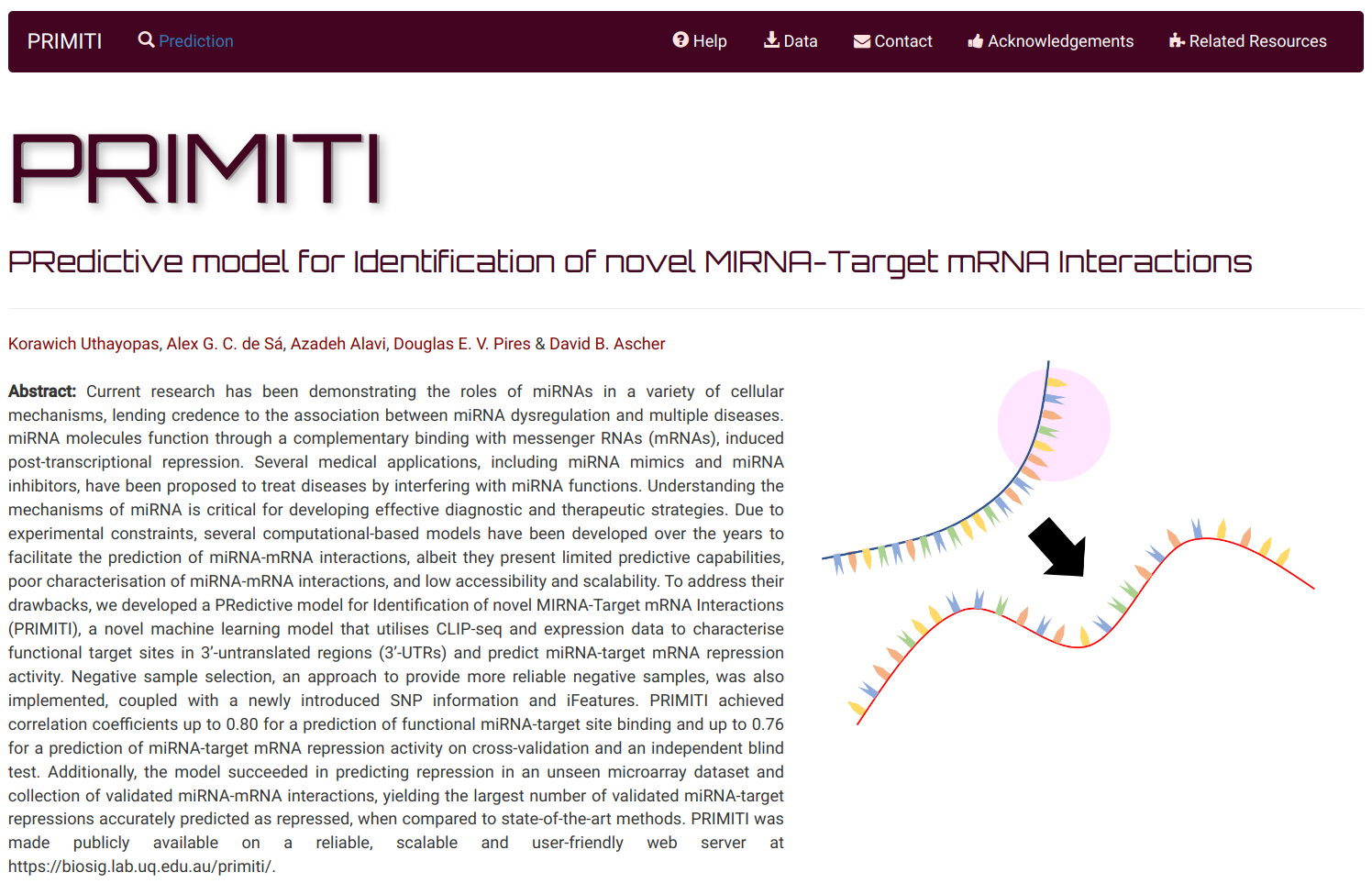
PRedictive model for Identification of novel MIRNA-Target mRNA Interactions (PRIMITI) is a novel machine learning model that utilises CLIP-seq and expression data to characterise functional target sites in 3’-untranslated regions (3’-UTRs) and predict miRNA-target mRNA repression activity
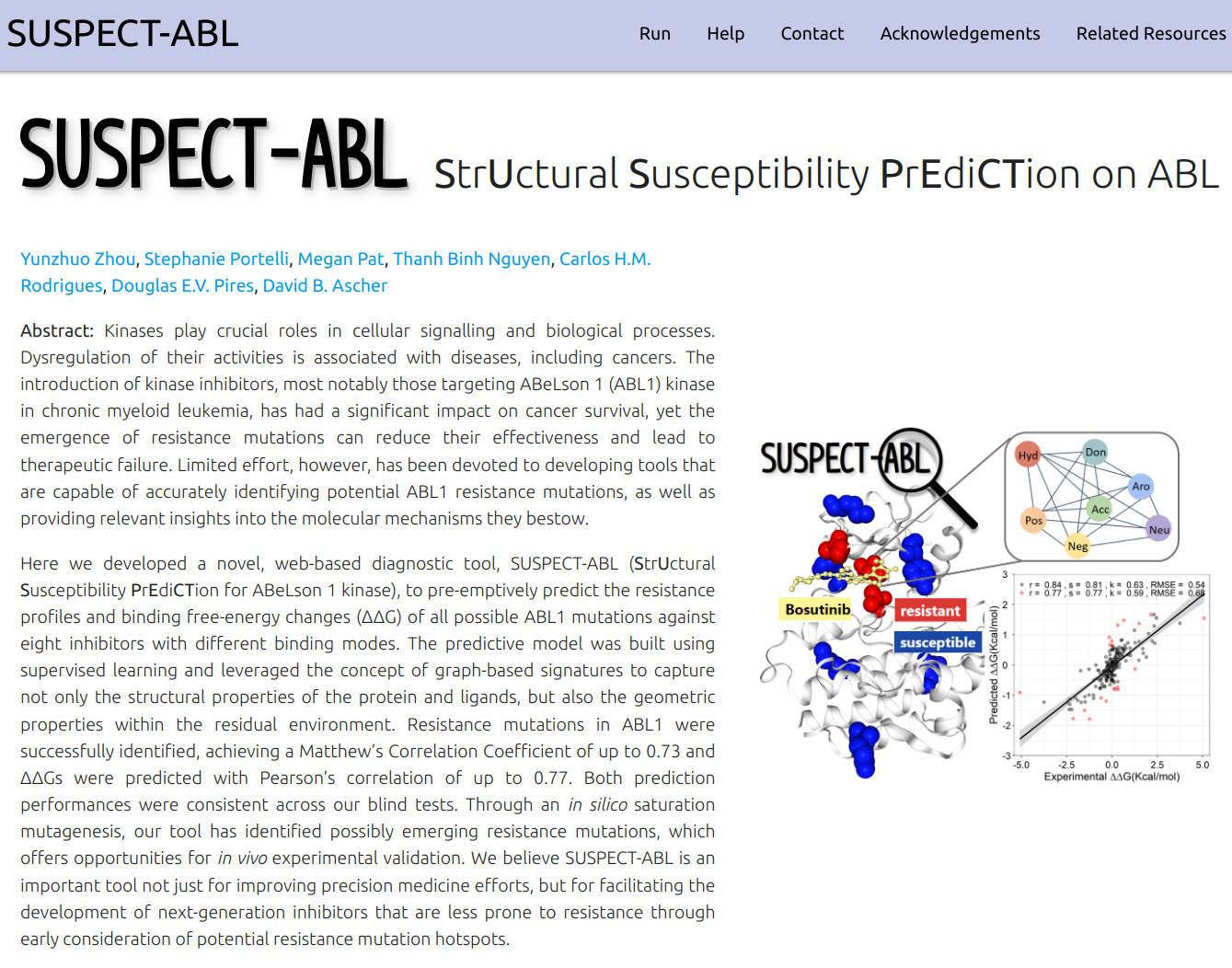
SUSPECT-ABL (StrUctural Susceptibility PrEdiCTion for ABeLson 1 kinase) is a novel, web-based diagnostic tool to pre-emptively predict the resistance profiles and binding free-energy changes (ΔΔG) of all possible ABL1 mutations against eight inhibitors with different binding modes
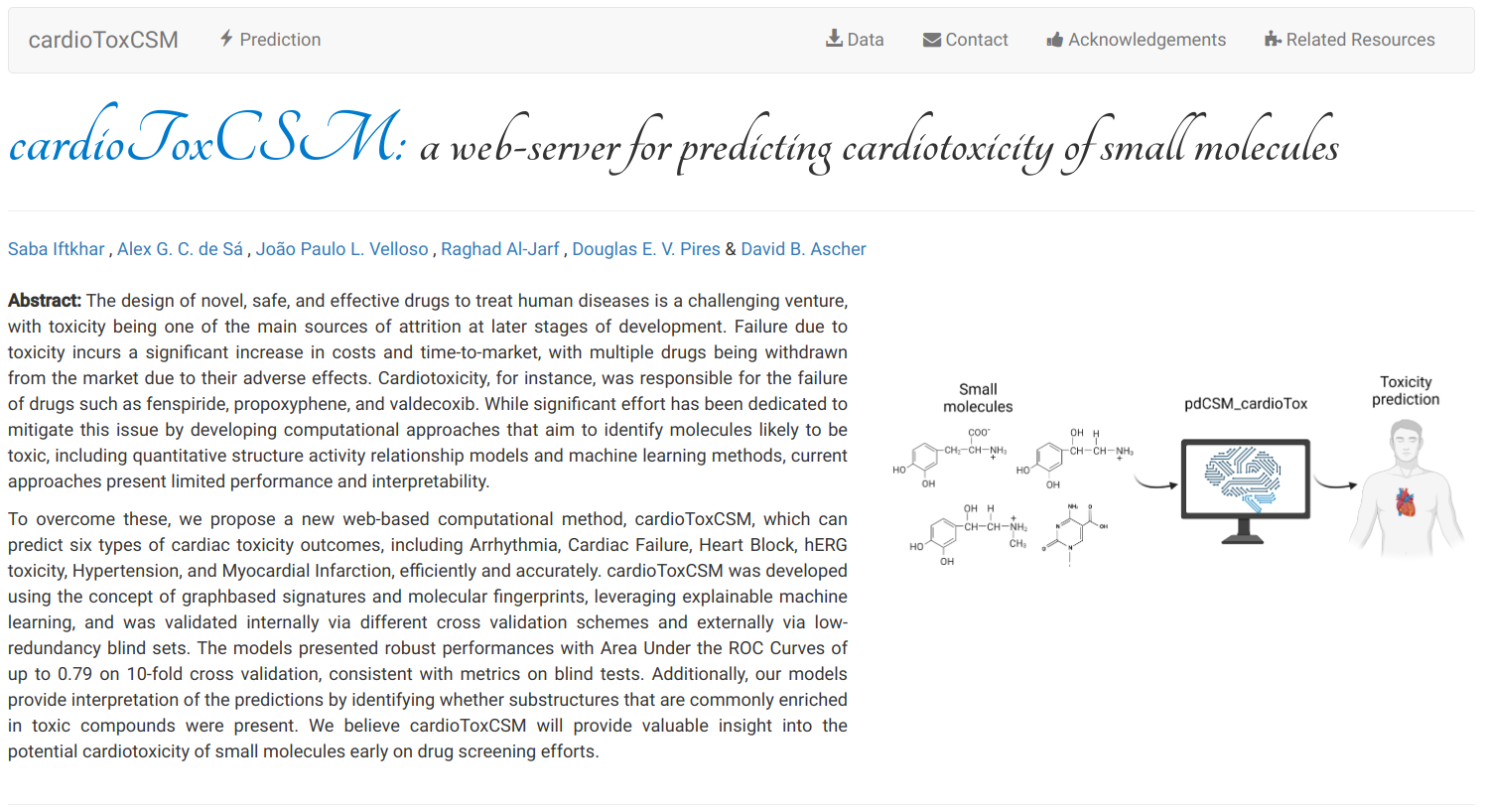
cardioToxCSM is a new web-based computational method which can predict six types of cardiac toxicity outcomes, including Arrhythmia, Cardiac Failure, Heart Block, hERG toxicity, Hypertension, and Myocardial Infarction, efficiently and accurately
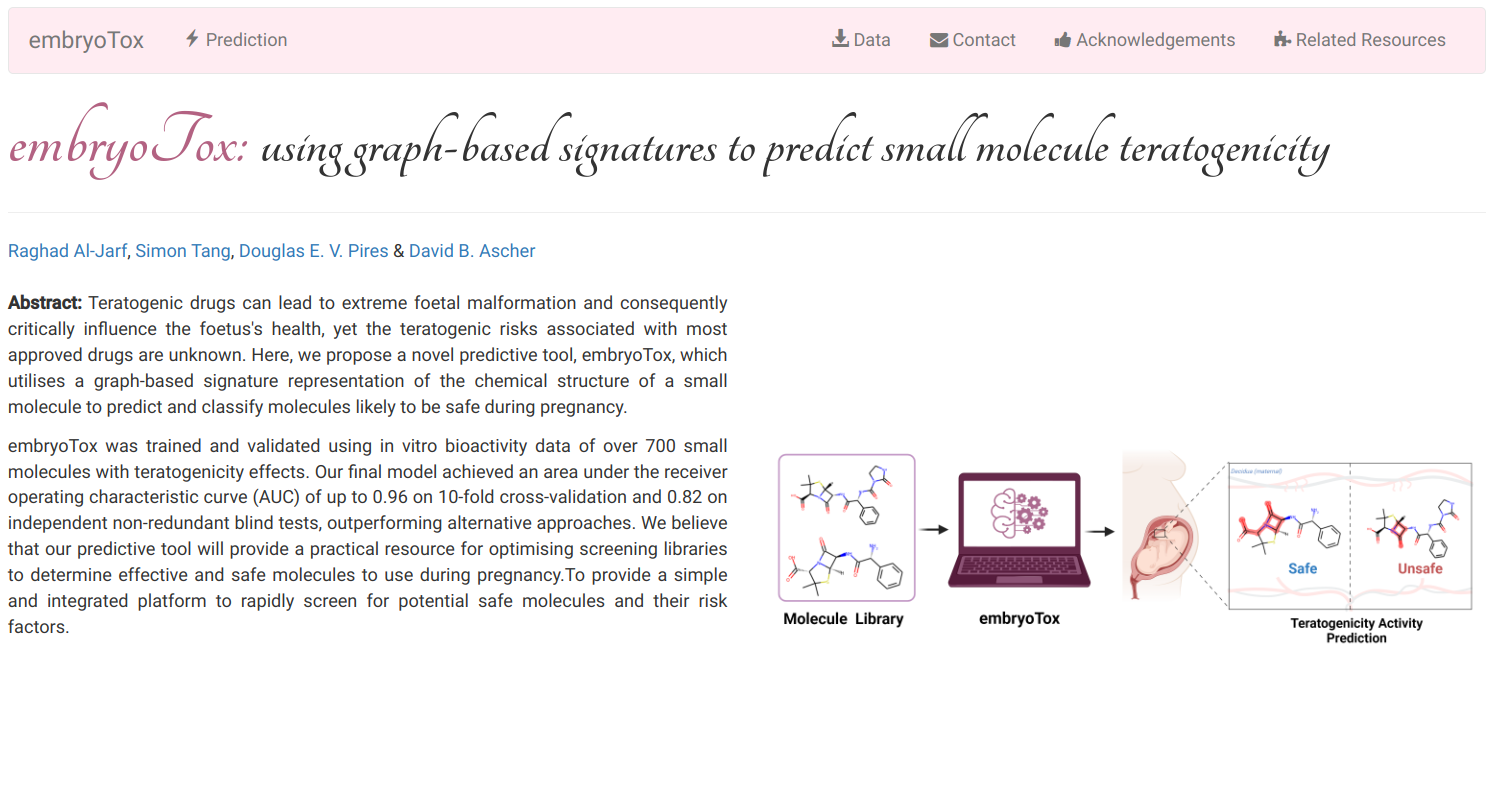
embryoTox is a novel predictive tool which utilises a graph-based signature representation of the chemical structure of a small molecule to predict and classify molecules likely to be safe during pregnancy

LEGO-CSM is a comprehensive web-based resource that leverages our graph-based signatures and uses protein sequence and/or structure to accurately model key aspects relevant to protein function characterisation: Localization, Enzyme Commision numbers and GO terms
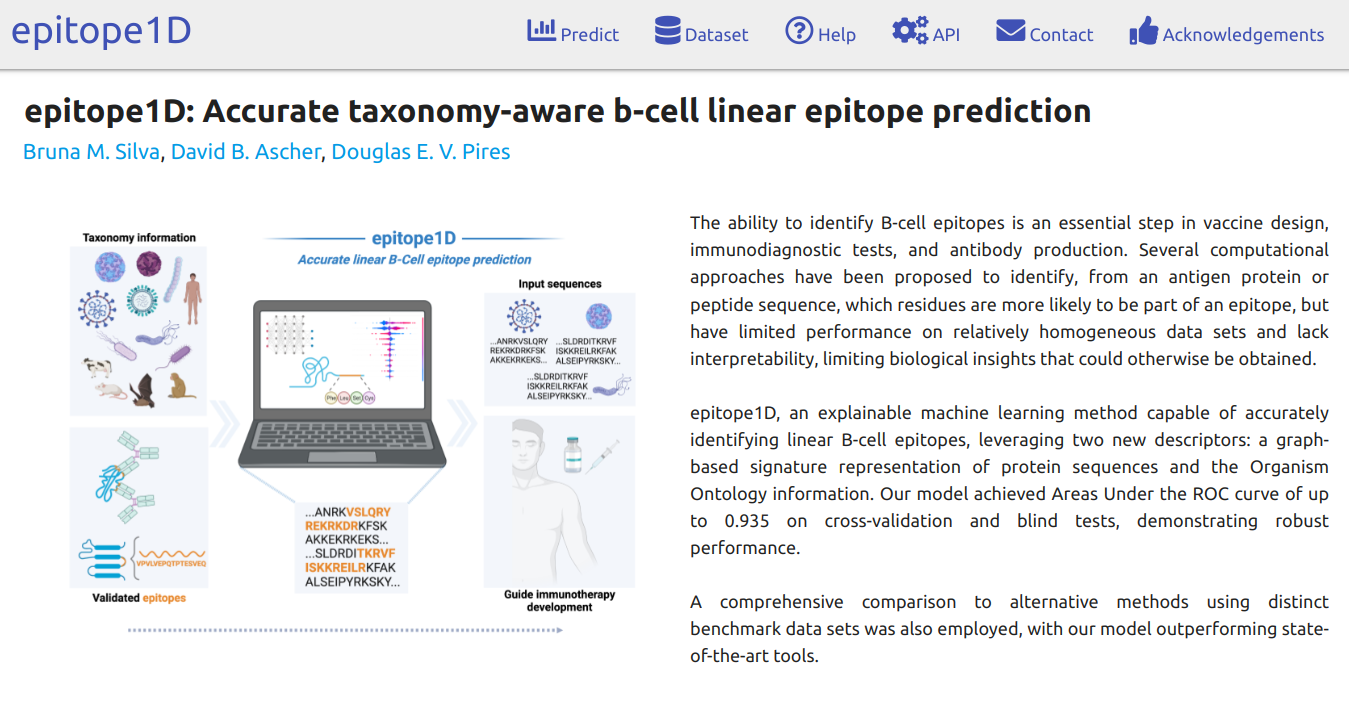
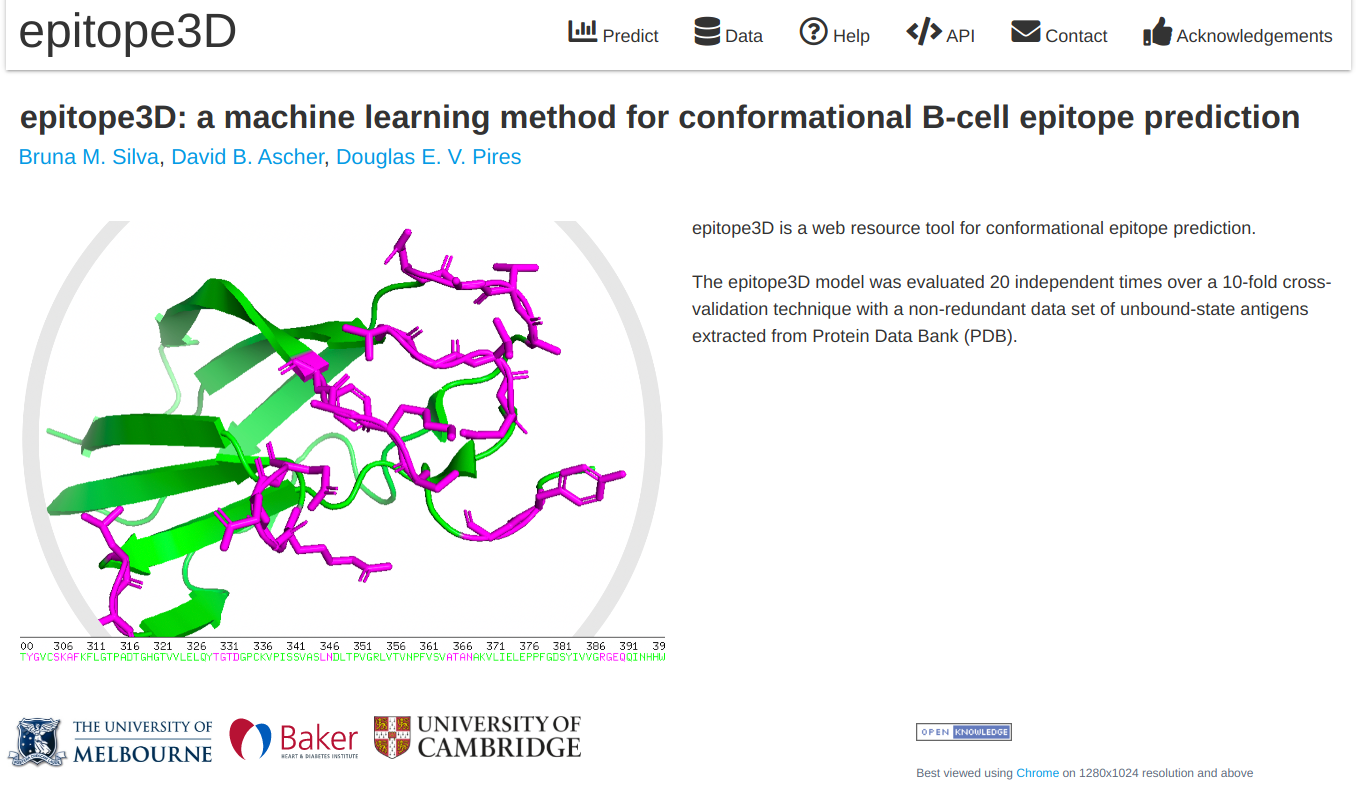
epitope1D, an explainable machine learning method capable of accurately identifying linear B-cell epitopes, leveraging two new descriptors: a graph-based signature representation of protein sequences and the Organism Ontology information.
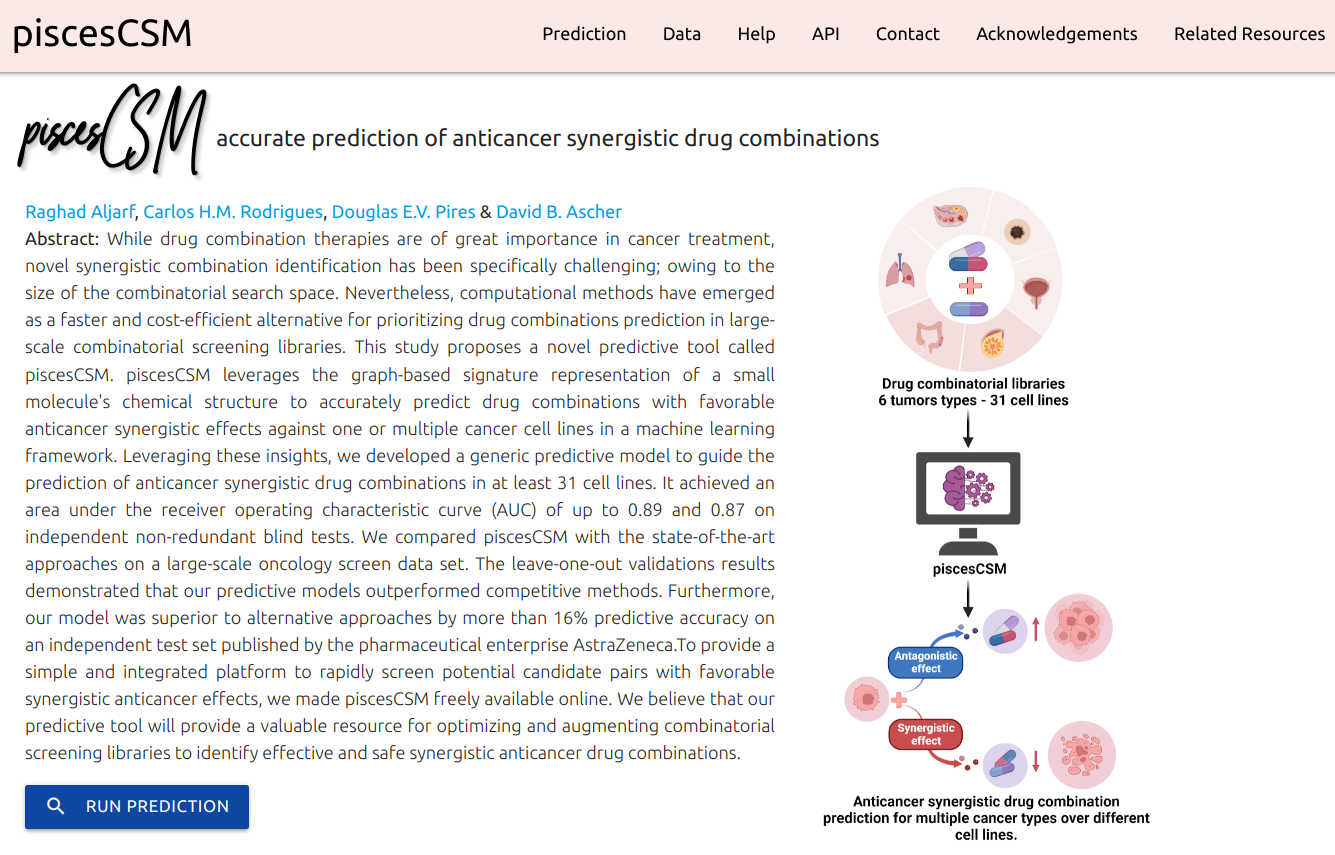
piscesCSM leverages the graph-based signature representation of a small molecule's chemical structure to accurately predict drug combinations with favorable anticancer synergistic effects against one or multiple cancer cell lines in a machine learning framework. Leveraging these insights, we developed a generic predictive model to guide the prediction of anticancer synergistic drug combinations in at least 31 cell lines.