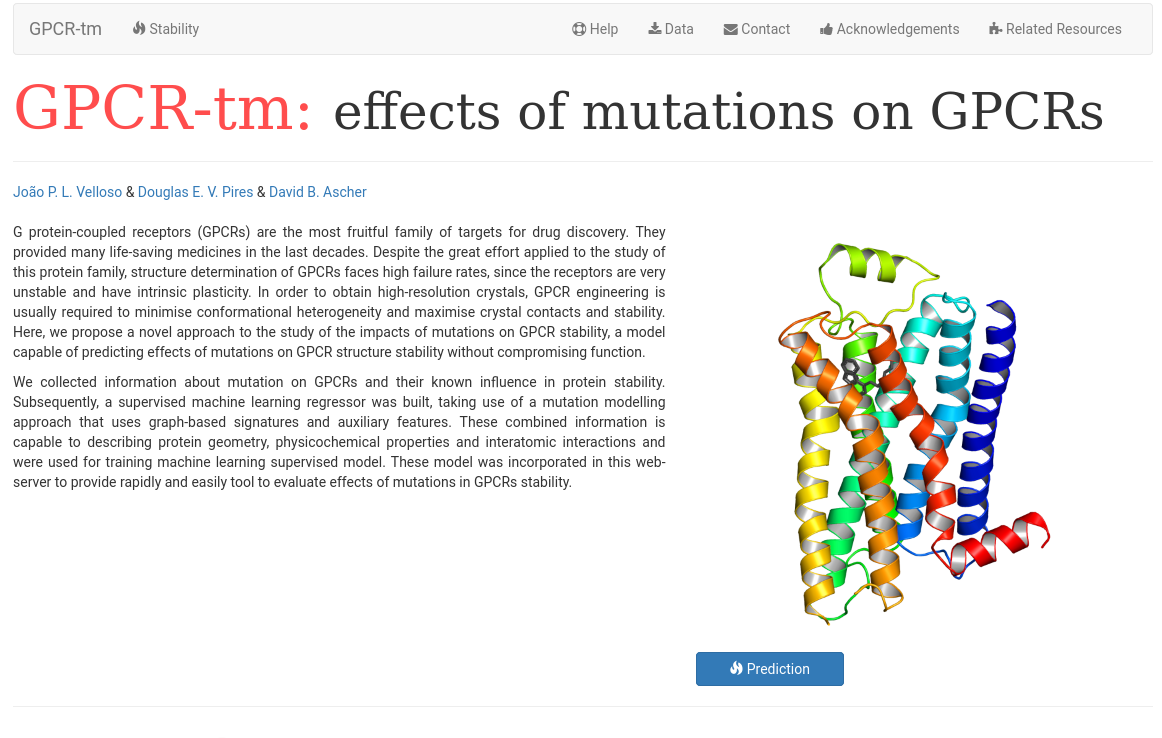
GPCR-tm: effects of mutations on GPCRs
Tip! GPCR-tm can be used with homology models.
Tip! Try using the key arrows in your keyboard or the buttons below to switch among the tips below.
Main page
About GPCR-tm
GPCR-tm is a user friendly web server that can be used to analyse the impacts of mutation on the stability of GPCRs. It is a machine learning approach that uses graph-based structural signatures to train and test predictive models. GPCR-tm represents a significant advance upon our current predictive platform, which has been built using globular soluble proteins, or membrane proteins by allowing the analysis of the effects of mutations on GPCRs exclusively. To analyse the effects of mutation on stability click in the Prediction button (bottom right).
Submission page
How to run a prediction
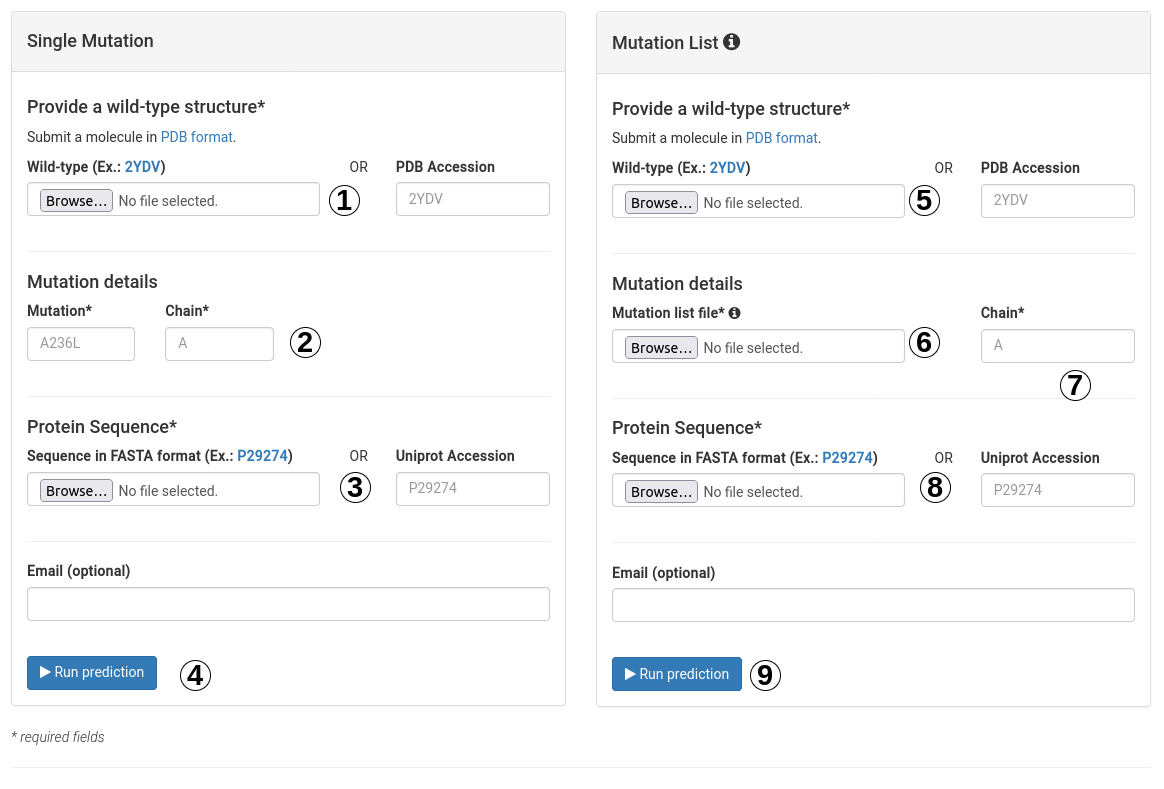
To run the prediction on a mutation list:- Provide the structure of the wild-type protein, which must comply with the PDB format by either providing a PDB accession code or by uploading your own structure (5).
- A file with a list of mutations to be analysed should be provided (6), with one mutation per line, following the aforementioned mutation format. The chain must also be provided and consistent with the PDB file (7).
- Provide the UNIPROT accession code for your protein protein (8).
- You are then ready to submit your query for analysis (9).
Results page
Results - List of Mutations
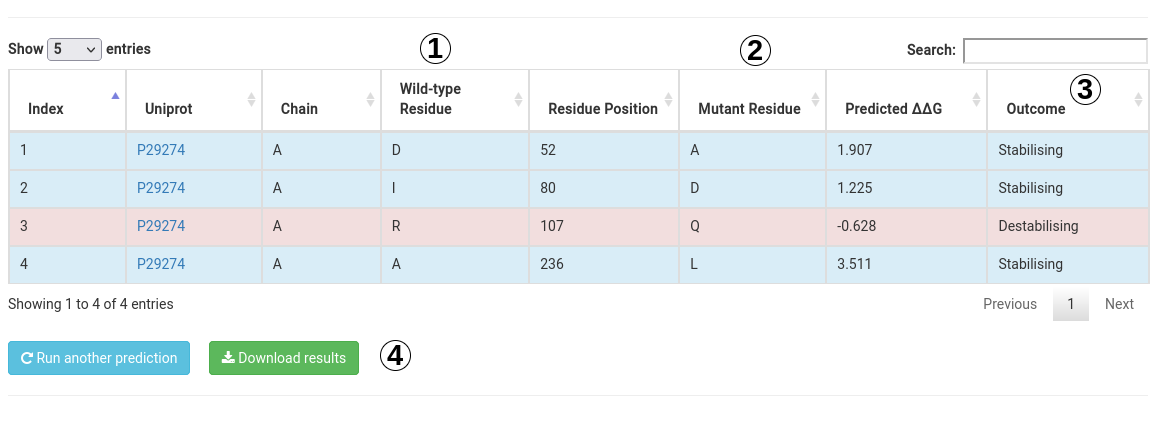
Your results for a list of mutations will be displayed in a table format with the following information:
- Mutantion information (1).
- The predicted effect (ΔΔG) (2) and the predicted outcome (3).
Contact page
Getting in touch
In case you experience any trouble using GPCR-tm or have any suggestions or comments, please do not hesitate in contacting us either via e-mail or through the online form.