AlzDiscovery Identifying Alzheimer's Disease-causing missense mutation
Qisheng Pan, Georgina Becerra Parra, YooChan Myung, Stephanie Portelli, Thanh-Binh Nguyen, David B. Ascher
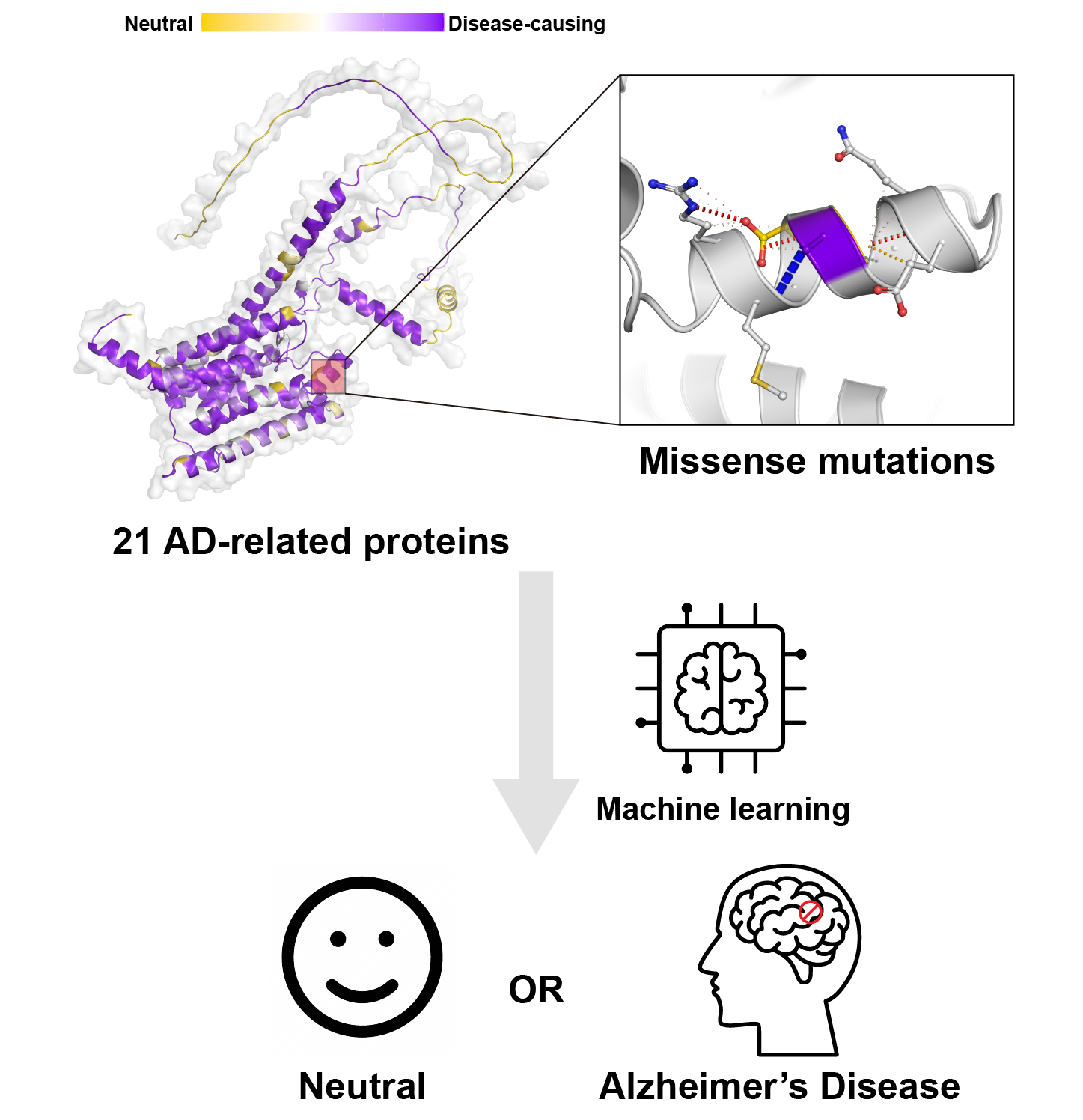
Abstract: Alzheimer's Disease (AD) is one of the most common dementia and neurodegenerative diseases, characterised by the formation of neuritic plaques and neurofibrillary tangles. Many different proteins participate in this complicated pathogenic mechanism, and missense mutations can largely alter the functions of these proteins, increasing the risk of AD. To identify the disease-causing mutations, we not only calculated the sequence-based features but also extracted structural descriptions of the mutations in AlphaFold2 models. Then we trained a machine learning model to classify the AD-causing mutations from the benign counterparts. By introducing structure-based information to our model, we are able to characterise the disease causing mutations with a generic predictive performance of MCC up to 0.74. Performance was further improved to 0.79 by tuning the sample weights in the training process, which show a comparable performance with the state-of-the-art methods. Feature interpretation techniques indicated the aliphatic residue environment, polar interaction contacts, and residue properties of the mutant amino acids were crucial to the pathogenicity of missense mutations. Finally, we presented a user-friendly web server, AlzDiscovery, for AD researchers to browse the predicted effect of all possible missense mutations on 21 AD-related proteins. This will be a valuable resource for monitoring of AD patients and the development of personalising treatment.